A new method for inferring drug effector cell types based on single-cell transcriptomic data
2024-06-02 | 药学院英文网
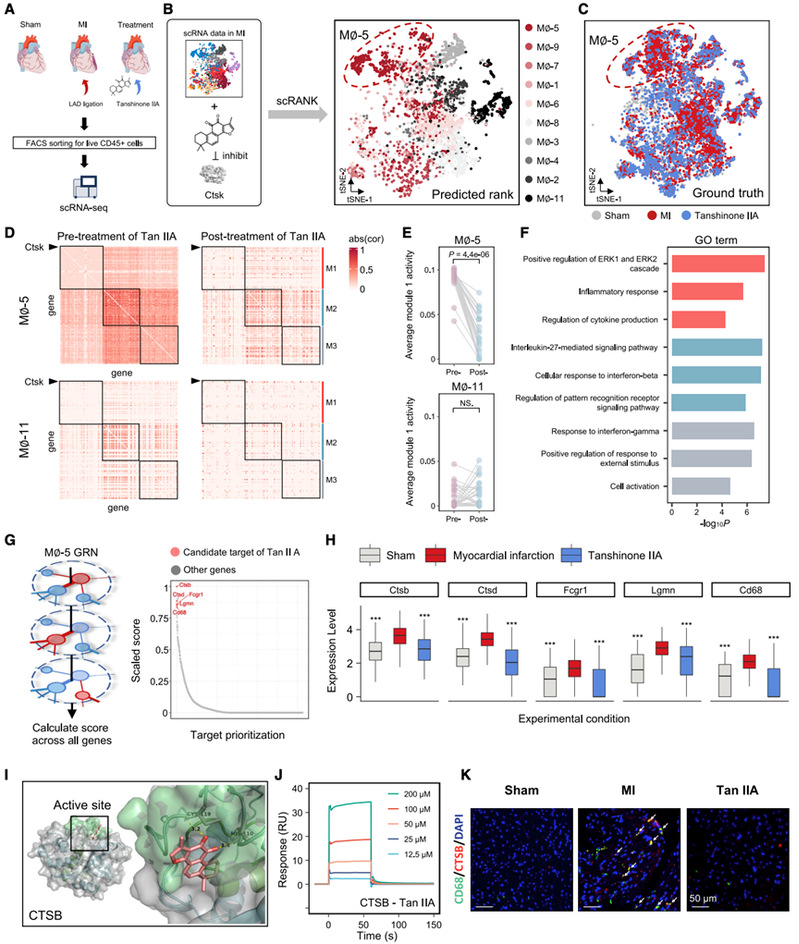
On May 15, 2024, the team of Prof. Yi Wang and Prof. Xiaohui Fan from College of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Zhejiang University published the paper scRank infers drug-responsive cell types from untreated scRNA-seq data using a target-perturbed gene regulatory network online in Cell Reports Medicine. data using a target-perturbed gene regulatory network. The paper utilizes a target-perturbed gene regulatory network (tpGRN) to model drug perturbation by integrating biological networks and drug target information, and achieves the inference of drug-responsive cell types from untreated single-cell transcriptome data only.

Using scRank, the research team successfully analyzed the mechanism of action of tanshinones in the blood-activating and blockage-removing traditional Chinese medicine Danshen, which has complex targets, and inferred the macrophage subpopulations that are mainly inhibited by tanshinone IIA in the process of relieving myocardial infarction. The study further demonstrated that scRank can reveal the potential molecular targets of traditional Chinese medicine and natural product molecules with complex targets. By inputting a known target of tanshinone IIA and a target macrophage subpopulation of tanshinone IIA, the research team was able to sequence the gene nodes of the macrophage subpopulation biological network and identify potential additional targets of tanshinone IIA. In summary, scRank can accurately infer the effector cell types and potential targets of drugs from unprocessed scRNA-seq data, which provides an important tool for understanding the mechanism of drug action at the single-cell level, and can provide a new research strategy for the identification of efficacy of complex systems of traditional Chinese medicines and precision therapy. scRank has been open-sourced to GitHub (https:/ / github.com), and is now available on GitHub (https:/ / github.com). /github.com/ZJUFanLab/scRank).

Chengyu Li, a PhD student of College of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Zhejiang University, and Xin Shao, a researcher of the Innovation Center of Yangtze River Delta, Zhejiang University, are the first authors. Prof. Yi Wang, Prof. Xiaohui Fan and Prof. Xin Shao from College of Pharmaceutical Sciences and National Key Laboratory of Modern Chinese Medicine are the corresponding authors.
NEWS
-
10
2025.12
-
27
2025.11
-
25
2025.11
-
03
2025.11
-
30
2025.10
-
29
2025.10
