Research from CHEN Shuqing's lab has been published in Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy
2021-09-18 | 药学院英文网
On Sept.3, Professor CHEN Shuqing and Principle Investigator PAN Liqiang published the newest research entitled A multivalent biparatopic EGFR-targeting nanobody drug conjugate displays potent anticancer activity in solid tumor models in Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy.

The epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), one member of the ErbB family of receptor tyrosine kinases, has been implicated in various epithelial malignancies. As a clinically validated target, both small-molecule tyrosine kinase inhibitors and antibody-based drugs have been approved by regulatory agencies. Anti-EGFR antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) could kill target tumor cells irrespective of EGFR signaling. However, cancer patients treated with EGFR-targeted antibody therapy eventually develop acquired epitope substitutions such as S492R, G465R, G465E, and I491M, which abolish cetuximab or panitumumab binding and further gives rise to resistance to anti-EGFR ADC therapy.1 Our team has constructed a tetravalent biparatopic anti-EGFR nanobody-drug, consisting of two tandemly fused anti-EGFR nanobodies (7D12 and 9G8) targeting two distinct non-overlapping epitopes (9G8-7D12-Fc, abbreviated as 97m). Coupling anti-mitotic agent monomethyl auristatin E (MMAE) to the conservative engineered surface cysteine S7C on 7D12 part of 97m resulting its conjugate, abbreviated as S7 ADC (Fig. 1a and Supplementary Fig. S1a–c). The tetravalent biparatopic ADC demonstrated high conjugation efficiency, small binding interfaces to overcome cetuximab-resistant mutations, enhanced complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC), and highly potent antitumor activity. The introduction of E430G in the Fc domain would further boost the complement-mediated immune response of S7 ADC, synergizing with the cytotoxicity of drug payload during cancer treatment.
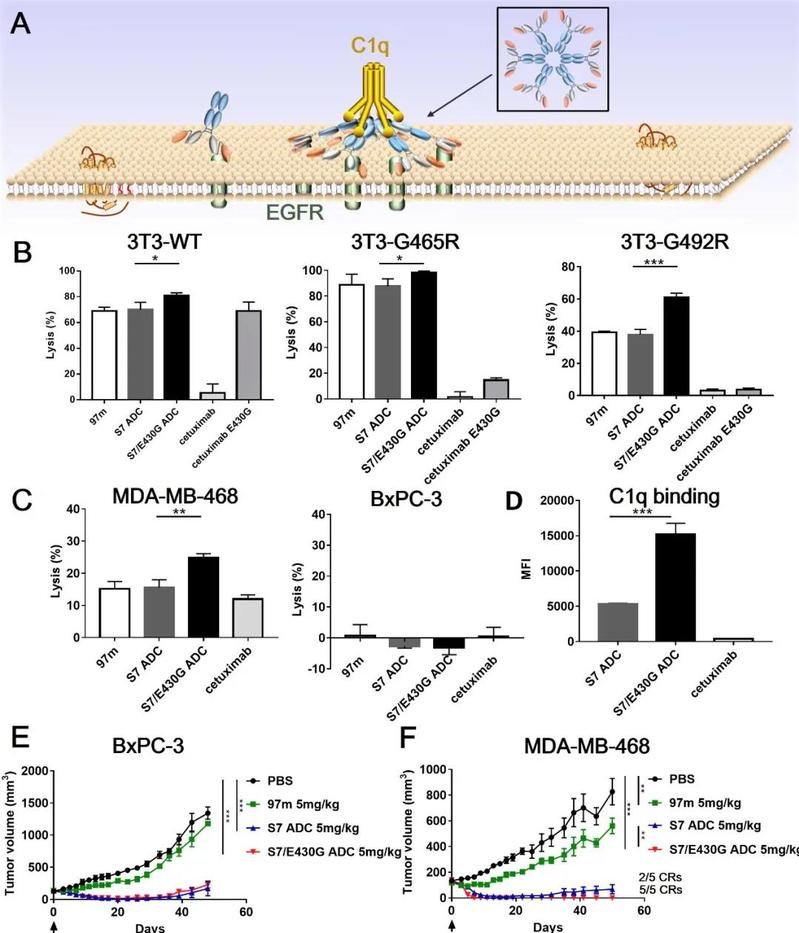
This work was carried out by Jiansheng Fan under the supervision of Professor CHEN Shuqing and Principle Investigator PAN Liqiang.
Link: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41392-021-00666-5
NEWS
-
10
2025.12
-
27
2025.11
-
25
2025.11
-
03
2025.11
-
30
2025.10
-
29
2025.10
